Active Record in Rails has simplified database table relations. It made it much easier for the backend developers to connect tables together whether it is many-to-many or one to one.
In this blog, I will show you a simple way how to create a many-to-many relationship in your backend rails project. Open your project and follow with me step by step to tackle this complicated challenge in other programming languages and frameworks.
Pick your models
Decide which models that have a many-to-many relationship. For example, the relationship between authors and books. An author has many books and, sometimes, a book belongs to many authors.
Create a join table
In any many-to-many relationship, you need a third table that is called a Join Table. You need this model/table to build the relationship using the primary key from each table resulting in a table with two foreign keys. For our example, the table will have author_id, and book_id. Here is a handy command to create the model and the migration for the joining table.
rails generate model AuthorBookFix your migration
The previous command generated an empty migration. You will have to fix the migration to include both primary keys of the two tables you are adding the relationship for.
class CreateAuthorBooks < ActiveRecord::Migration[6.0]
def change
create_table :author_books do |t|
t.integer :author_id
t.integer :book_id
t.timestamps
end
end
endCreate the table
You didn’t create the table yet. You only created the migration that when you run this migration, the table will be created.
rails db:migrateFix your models
You have to specify the relationship for each of the models that are related to this process. For our example, the Author model, the Book model, and the AuthorBook model.
- AuthorBook model:
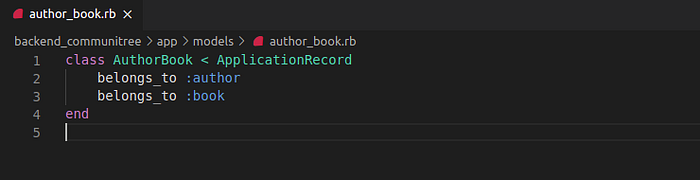
The AuthorBook model belongs to both tables and we specify this as follow:
class AuthorBook < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author
belongs_to :book
end- Author model:
The Author model has many books through the joining table, AuthorBook, and also has many author_book:
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :author_books
has_many :books, through: :author_books
end- Book model:
The Book model has many authors through the joining table, AuthorBook, and also has many author_book:
class Book < ApplicationRecord
has_many :author_books
has_many :authors, through: :author_books
endAlternative Way
You could even use another simpler way to declare this relationship by using “has_and_belongs_to_many” macros for each of the author and book models. You still need only the joining table for the relationship to work, but no need for the model.
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :books
end
class Book < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :authors
end
And that's how you declare a many-to-many relationship in Rails. If you have anything you would like to add, please comment below.
